Leave Your Message
In the rapidly evolving landscape of network technology, "10G DWDM 80km" stands out as a beacon for enhancing bandwidth efficiency. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) technology enables the transmission of multiple signals simultaneously over a single fiber. Reports indicate that global internet traffic is expected to increase by 30% annually. This growth underscores the need for robust and efficient solutions like 10G DWDM.
Implementing 10G DWDM systems for distances up to 80km can significantly optimize network performance. Studies show that these systems can support over 80 channels, effectively quadrupling the data capacity of traditional systems. However, challenges remain. Many organizations struggle with integration and deployment costs. Furthermore, maintaining signal integrity over distance can be complex, requiring careful planning and monitoring.
Despite these obstacles, the benefits of 10G DWDM 80km are compelling. Enhanced capacity supports high-demand applications like cloud services and video streaming. A well-optimized network can dramatically improve user experience and operational efficiency. As we move forward, reflecting on these challenges will be crucial for leveraging this valuable technology. Adapting to the needs of today’s digital world is key to unlocking the full potential of network infrastructures.

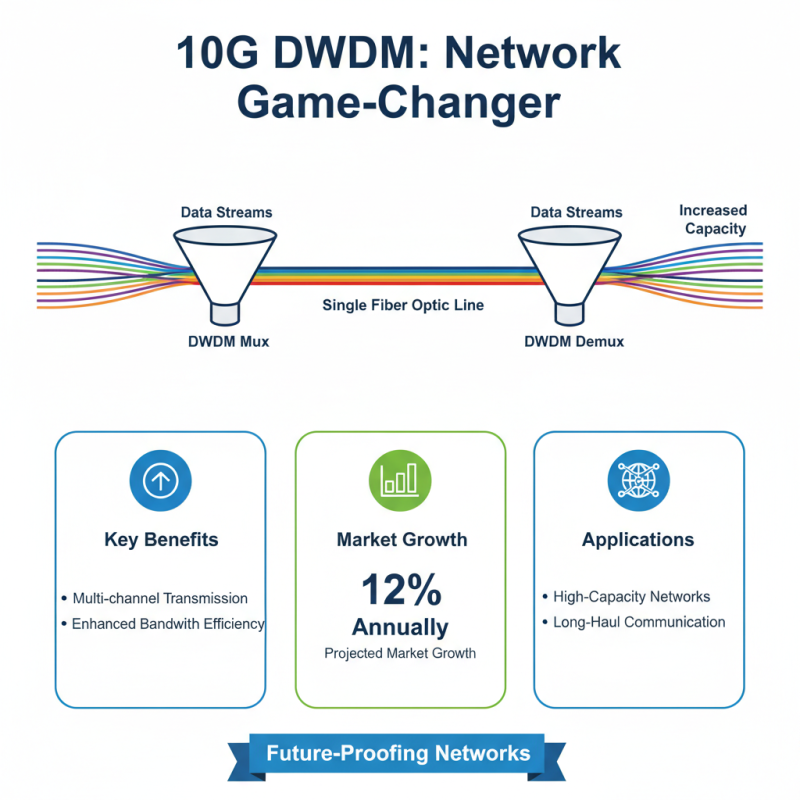
10G DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technology is a game-changer for network performance. It allows multiple data streams to travel simultaneously over a single fiber optic line. According to a report by market research, the DWDM market is projected to grow by 12% annually, highlighting its increasing adoption in high-capacity networks. This technology effectively uses channel spacing that can differ from other methods, thus enhancing bandwidth efficiency.
Over a distance of 80km, 10G DWDM systems can deliver capacity scaling effectively. With this setup, operators can handle massive data loads typical in cloud services and telecommunication. Enhanced signal integrity and lower latency are significant benefits of this technology. However, it is worth noting that achieving optimal performance requires precise tuning and monitoring of the optical network. Regular assessments can highlight areas for improvement, ensuring systems function at peak performance levels.
One challenge is the initial setup cost, which can be high. Organizations may hesitate to invest without a clear understanding of long-term gains. Also, not all installations guarantee an immediate upgrade in performance. Reflections on operational needs are crucial. Assessing the expected return on investment can help guide decisions.
In modern telecommunications, 80km is a significant reach for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) networks. This distance allows operators to connect regional hubs with ease. The demand for high-capacity and long-distance transmission is growing. In fact, industry reports suggest that the global DWDM market is expected to grow by 16% annually over the next five years.
One of the key features of 80km DWDM systems is their ability to transmit data with minimal signal loss. Quality optics play a crucial role here. With advanced EDFA (Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier) technology, signals can be boosted efficiently. This minimizes the need for additional repeaters and reduces latency.
However, it’s essential to note that while 80km is a landmark capability, network planners must consider environmental factors. Fiber cable degradation can be influenced by temperature and humidity. Regular assessments of the fiber's condition are necessary to avoid unexpected failures. Real-time monitoring systems can address some of these challenges, ensuring optimal performance over time.
The 10G DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) system is crucial for enhancing network performance over long distances. It enables organizations to transmit multiple data streams simultaneously through a single optical fiber. To truly grasp its effectiveness, one must consider several key components involved in these systems.
First, optical amplifiers are vital in maintaining signal strength over extensive ranges, such as 80 kilometers. According to the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, using erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) can boost signal power by up to 30 dB. However, inefficient use of these amplifiers can lead to signal degradation, making careful analysis essential.
Another critical component is the multiplexers and demultiplexers. They facilitate the separation and combination of wavelengths. A well-designed mux can support more than 80 wavelengths, but the complexity increases with each additional channel. In practice, ensuring that these components work seamlessly together often proves challenging. Bandwidth management tools are also necessary. They help in monitoring and adjusting the flow of data, yet many enterprises still struggle with optimizing these tools for their specific needs. Ultimately, understanding these components is key to leveraging the full potential of 10G DWDM technology.
| Component | Description | Specification | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transmitter | Uses external modulation to increase signal quality | 10 Gbps, 1550 nm | Optical Output Power: -10 dBm |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Single-mode fiber designed for long-distance transmission | 80 km length, 9/125 μm core/cladding | Attenuation: 0.2 dB/km at 1550 nm |
| Multiplexer | Combines multiple wavelengths for transmission | Wavelengths: 1530-1565 nm | Channel Spacing: 100 GHz |
| Demultiplexer | Separates combined wavelengths back into individual signals | Wavelengths: 1530-1565 nm | Insertion Loss: < 1.5 dB |
| Receiver | Converts optical signals back to electrical signals | 10 Gbps, Sensitive to < -20 dBm | Bit Error Rate: < 10^-12 |
| Amplifier | Boosts signal strength over long distances | EDFA, 1530-1565 nm | Gain: 20 dB |

Implementing 10G DWDM over 80km requires careful planning. Begin with accurate assessments of your existing infrastructure. This ensures you understand current limitations. Upgrading fiber and equipment is often necessary. Engage with network specialists if needed. They can provide insights into potential bottlenecks.
Design your network layout strategically. It’s important to consider the placement of nodes and amplifiers. Each kilometer can introduce attenuation. Use tools to monitor signal strength along the route. Regular assessments will reveal weak links. Document these findings for future upgrades.
Train your team on the specifics of DWDM systems. Knowledge gaps can lead to implementation errors. Conduct regular workshops or training sessions. Encourage discussions about challenges faced during deployment. Reflection on past experiences can refine the process. Consider feedback seriously to enhance overall performance.
The evolution of 10G DWDM technology unlocks new potential for network performance. Future trends focus on scaling capacity while minimizing cost. The demand for bandwidth continues to surge. Advanced modulation techniques emerge as a solution. These methods enhance data rates and transmission distance. This transformation is crucial for adapting to increased data traffic.
Tips: Monitor network performance closely. Identify bottlenecks using analytical tools. Regular assessments can reveal areas needing upgrade.
Emerging technologies like software-defined networking (SDN) will change the way we optimize. SDN allows for better resource allocation. It simplifies network management and improves efficiency. This tech can dynamically adjust to traffic conditions, improving the overall network experience.
Tips: Conduct regular training for your tech team. Stay updated on trends. This will allow for quick adaptation and proactive decision-making.
Exploring new wavelengths and exploring innovative designs is vital. The goal is always optimal performance without overspending. Reflection on current limitations helps in addressing future challenges effectively. Adaptation is key in this rapidly changing landscape.






