Leave Your Message
Implementing 10G DWDM for an 80km distance offers significant advantages. High data rates and enhanced capacity drive modern networks. However, challenges arise during implementation. Proper planning and equipment selection are crucial.
Engineers must choose suitable components tailored for 10G DWDM 80km applications. Fiber quality, amplifier placement, and signal integrity greatly impact performance. Balancing these factors defines project success. Communication with team members becomes vital, as multiple perspectives enhance problem-solving.
Real-world scenarios can deviate from idealized plans. Potential issues may include unexpected signal loss or interference. These situations require quick thinking and adaptability. A thorough understanding of the technology helps mitigate risks. Observing and learning from past projects improves future implementations. Embracing the complexity of 10G DWDM for 80km drives innovation and growth.

Understanding 10G DWDM technology is crucial for long-distance communication. This technology uses dense wavelength division multiplexing to maximize data transmission. With 10G DWDM, multiple data signals share the same fiber. This efficiency is especially important for networks covering distances like 80km.
Recent industry reports indicate that the global DWDM market is growing rapidly. It is projected to reach over $20 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing importance of efficient data transfer. Long-distance communication demands reliability and speed. 10G DWDM offers this by allowing high-capacity connections without significant signal loss.
**Tip:** When planning to implement 10G DWDM, ensure thorough network assessment. Consider factors like existing infrastructure and environmental conditions.
However, challenges exist. Not all fibers can support high-capacity wavelengths. Spacing and channel alignment issues may arise. These challenges require careful planning and ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal performance.
**Tip:** Engage with industry experts to address potential hurdles. Early intervention can save time and resources.
Cost is another concern. Upfront investment in technology can be substantial. Organizations need to analyze the long-term benefits versus initial costs. Balancing budgeting with performance is essential for successful deployment.
When implementing 10G Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) for an 80km distance, key components play a crucial role. Optical transceivers are essential. These devices convert electrical signals into optical signals. A good optical amplifier will also be needed. It boosts the signal strength, ensuring reliable data transmission over the distance.
The optical fibers should be chosen carefully. Single-mode fibers are ideal for this application. They minimize signal loss and allow for high data rates. You might also need wavelength multiplexers and demultiplexers. These devices manage the multiple channels in the system. They help to combine multiple signals onto a single fiber. However, not all configurations work perfectly. You may face issues like crosstalk or signal degradation if not set up correctly.
Monitoring equipment is equally important. It helps track signal quality and performance. Regular checks prevent outages and ensure optimal operation. Sometimes, environmental factors can also affect performance. Installing in a suitable setting minimizes these risks. Designing a DWDM system is complex and requires careful planning. Mistakes can lead to costly downtimes. Engaging experts can improve implementation success but does not guarantee perfection.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) | Installation Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10G DWDM Transponder | Device to convert electrical signals to optical signals for transmission. | $1,000 | 1 day |
| Optical Amplifier | Enhances the optical signal for long-distance transmission. | $2,500 | 1 day |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Single-mode fiber optic cable suitable for 80km distance. | $3,000 | 2 days |
| Multiplexer/Demultiplexer | Combines multiple signals into one fiber and separates them at the receiving end. | $1,500 | 1 day |
| Network Management System | Software for monitoring and managing the DWDM network performance. | $800 | 1 day |
When considering 80km DWDM deployments, evaluating fiber optic standards is crucial. Various standards exist, each focusing on different aspects of performance. Understanding these standards helps in making informed choices.
One widely used standard for long-distance transmission is ITU-T G.694.1. It outlines the specifications for wavelength division multiplexing. This standard can accommodate multiple channels, enhancing data capacity. Yet, deploying such technology requires careful assessment. Signal degradation over long distances can pose challenges.
Another important aspect is the selection of the fiber itself. Single-mode fibers often perform better for 80km distances. However, not all fibers are created equal. Some manufacturers may have better manufacturing practices. Research and testing are essential to ensure the best quality. It's this attention to detail that reflects a commitment to reliability. Various environmental factors also need consideration. Understanding how temperature fluctuations affect performance is vital. In this field, there's always room for reflection and improvement.
When deploying a 10G DWDM system for an 80km distance, careful attention must be paid to the link budget. Link budget calculations involve assessing various factors. These factors include transmitter power, fiber loss, and receiver sensitivity. A typical single-mode fiber has a loss of about 0.2 dB/km. For 80km, total fiber loss reaches approximately 16 dB.
Additionally, consider connector and splice losses, which can contribute around 1 dB to the overall budget. If the transmitter’s output power is 10 dBm and the receiver's sensitivity is -28 dBm, the margin shrinks. Thus, your link budget shows a net gain of 10 dB, which is often insufficient for real-world conditions.
Signal integrity must also be prioritized. Factors like chromatic dispersion and polarization mode dispersion can degrade the signal over long distances. According to the Telecommunications Industry Association, chromatic dispersion can reach 16 ps/nm/km in certain scenarios. This presents additional challenges. Solutions include using dispersion-compensating fibers or advanced modulation formats. However, these solutions can introduce complexity and increase costs. Analyzing these implementations can help ensure a robust, high-quality signal over the desired distance.
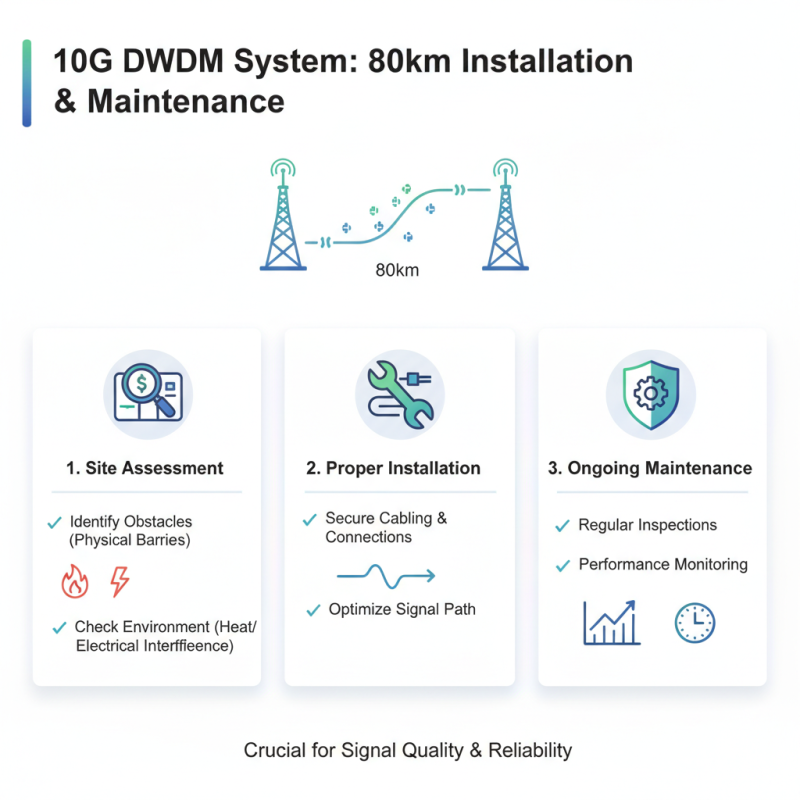
When implementing a 10G DWDM system over an 80km distance, proper installation and maintenance are crucial. Start with site assessment. Identify potential obstacles and ensure that the installation environment is up to standards. Look for physical barriers. Check heat sources and electrical interference. These factors can severely affect signal quality.
Once the installation begins, focus on proper cable management. Avoid tight bends that could cause signal degradation. Use appropriate enclosures to protect the equipment from dust and moisture. Regular maintenance checks are just as important. Inspect fiber connections routinely to prevent issues before they arise. Keeping an updated log of maintenance activities is essential. It can help track patterns and identify recurring problems.
Despite thorough planning, challenges may occur. Unexpected outages can disrupt service. Analyze the root cause and address it promptly. Seek input from team members to get diverse perspectives on recurring issues. Continuous learning is vital. Reflect on incidents and adjust practices accordingly. Every step taken strengthens the overall system reliability.






